-
Załączniki bezpieczeństwa
Załczniki do produktuZałączniki dotyczące bezpieczeństwa produktu zawierają informacje o opakowaniu produktu i mogą dostarczać kluczowych informacji dotyczących bezpieczeństwa konkretnego produktu
-
Informacje o producencie
Informacje o producencieInformacje dotyczące produktu obejmują adres i powiązane dane producenta produktu.
-
Osoba odpowiedzialna w UE
Osoba odpowiedzialna w UEPodmiot gospodarczy z siedzibą w UE zapewniający zgodność produktu z wymaganymi przepisami.
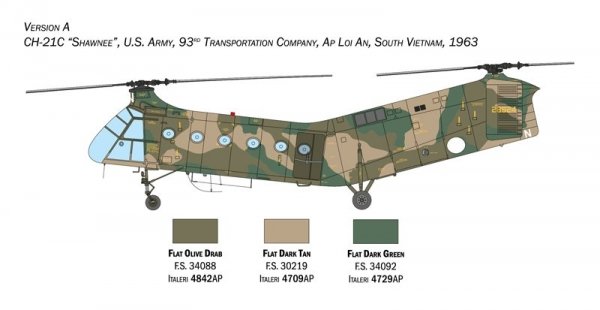
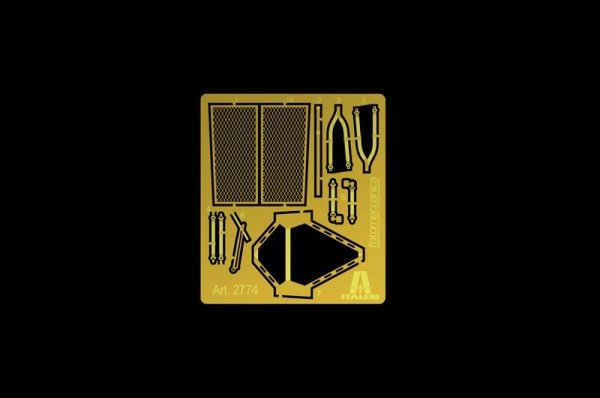
Italeri 2774 H-21C "Flying Banana" Gunship (1:48)
Plastikowy model do sklejania. Nie zawiera kleju ani farb.
Piasecki H-21 Shawnee/Workhorse (znany też jako CH-21) – amerykański dwuwirnikowy śmigłowiec transportowy zaprezentowany w 1949 roku przez przedsiębiorstwo Piasecki Helicopter. Śmigłowiec z powodu charakterystycznego wyglądu określany był mianem "latającego banana".
Śmigłowce H-21 Shawnee były wykorzystywane m.in. podczas wojny algierskiej przez Francuzów oraz podczas wojny wietnamskiej.
The Piasecki H-21 Workhorse/Shawnee is an American helicopter, the fourth of a line of tandem rotor helicopters designed and built by Piasecki Helicopter (later Boeing Vertol). Commonly called "the flying banana", it was a multi-mission helicopter, utilizing wheels, skis, or floats.
The H-21 was originally developed by Piasecki as an Arctic rescue helicopter. The H-21 had winterization features permitting operation at temperatures as low as −65 °F (−54 °C), and could be routinely maintained in severe cold weather environments.
Piasecki Helicopter designed and successfully sold to the United States Navy a series of tandem rotor helicopters, starting with the HRP-1 of 1944. The HRP-1 was nicknamed the "flying banana" because of the upward angle of the aft fuselage, which ensured that the large rotors could not strike the fuselage in any flight attitude. The name was later applied to other Piasecki helicopters of similar design, including the H-21.
In 1949, Piasecki proposed the YH-21 Workhorse to the United States Air Force (USAF), which was an improved, all-metal derivative of the HRP-1. Using two tandem, fully articulated three-bladed counter-rotating rotors, the H-21 was powered by one nine-cylinder Curtis-Wright R-1820-103 Cyclone supercharged 1,150 hp (858 kW) air-cooled radial engine.
After the first flight of the YH-21 on 11 April 1952,[1] the USAF ordered 32 H-21A SAR models and 163 of the more powerful H-21B assault transport variant. The H-21B was equipped with an uprated version of the Wright 103 engine, developing 1425 shaft horsepower (1063 kW), and featured rotor blades extended by 6 inches (152 mm). With its improved capabilities, the H-21B could carry 22 fully equipped infantrymen, or 12 stretchers, plus space for two medical attendants, in the medevac role. With its Arctic winter capabilities, the H-21A and H-21B were put into service by both the USAF and the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) to maintain and service DEW (Distant Early Warning) radar installations stretching from the Aleutian Islands and Alaska across the Canadian Arctic to Greenland and Iceland.




















 1 szt.
1 szt.
 2 szt.
2 szt.


 79 szt.
79 szt.